Making Playas Profitable Workshop
Want to know more about playas, the benefits they provide, and how to manage them as part of a profitable operation? Learn that and more at the 7th Annual Playa …
Playas provide clean water for Kansans and habitat for wildlife. By conserving playas, you can help them continue to work for Kansas—for generations to come.
Playa Benefits YOUR OPTIONSPlayas provide important wildlife habitat, but they also provide many benefits for people such as cleaner water going back into the Ogallala aquifer that can support families and towns, recreational activities, and flood control.

Playas are a primary source of groundwater recharge, with an average rate across the region of about three inches per year.

Playas are water filtration systems—keeping fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides out of the groundwater.

Playas attract wildlife, providing local waterfowl and upland game bird hunting and wildlife viewing opportunities.

Playas collect runoff during high rains, reducing property damage from flooding and reducing erosion.
Want to know more about playas, the benefits they provide, and how to manage them as part of a profitable operation? Learn that and more at the 7th Annual Playa …
Bids are now being accepted for a USDA program designed to provide landowners a market-based financial incentive for restoring playa wetlands. The Kansas USDA Farm Service Agency and several partners …
The May 2021 issue of Discover Magazine included an article, These Wetlands Feed The Largest Aquifer In The U.S. What Happens If We Lose Them?, which highlights the importance of playas to groundwater recharge.
Watch these videos to learn why agricultural producers in western Kansas are restoring and preserving their playas. Each video features a farmer or rancher talking about the benefits they receive by enrolling their playas in conservation programs—from financial returns, hunting habitat, and groundwater recharge to preserving history and leaving a legacy for future generations.
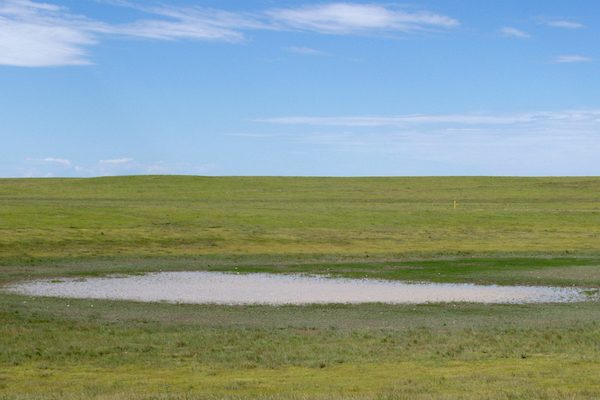
Playas—also called mud holes, buffalo wallows, and lagoons—are relatively small, round, shallow depressions found primarily in the western Great Plains. Their basins are lined with clay soil, which collects and holds water from rainfall and runoff, creating temporary lakes.

The extreme wet-dry cycle that playas experience is the lifeblood of their ecosystem. When dry, the clay soils contract and form large cracks in the bottom of the playa basin. Plant seeds and invertebrate eggs from the last wet period lay dormant in the soil, waiting for the next large rainfall to germinate and hatch. When the rain comes, the first flush of water runs into the playa and through the cracks, beginning its journey to the underlying aquifer. As the runoff continues, the clay soils expand; the cracks seal and the playa begins to fill with water. Wetland plants and invertebrates complete their life-cycle, and birds and mammals use the playa for food, water, and shelter.

In this grassland landscape, playas are the main source of water, providing much-needed rest stops and food to migrating waterfowl and shorebirds as well as resident prairie birds. Playas are the center of biodiversity on the plains—supporting 185 bird species, 450 plant species, 13 amphibian species, and 37 mammal species at some point in their life-cycle.

The greatest continuing threat to playas is culturally-accelerated sediment accumulation from row-crop agriculture. These sediments may interfere with the shrinking and swelling of the clay layer, which is vital to aquifer recharge, and reduce playa volume and length of time a playa will hold water, which significantly affects the plant and wildlife community supported by the playa. Modifications such as pits, ditches, berms, and roads also pose a threat to playas. These modifications concentrate water in a smaller area, thus reducing suitable habitat for water-dependent birds.
Playa Lakes Joint Venture held a Playa Recharge Summit with scientists and researchers who study various aspects of playas to determine what is known about groundwater recharge through playas. Click on a photo below to read what they had to say.



Use the Playa Recharge and Wetness Estimators to explore the playa landscape, calculate an estimate of how much water recharges through individual playas, and learn about past patterns of wetness for playas in different seasons.
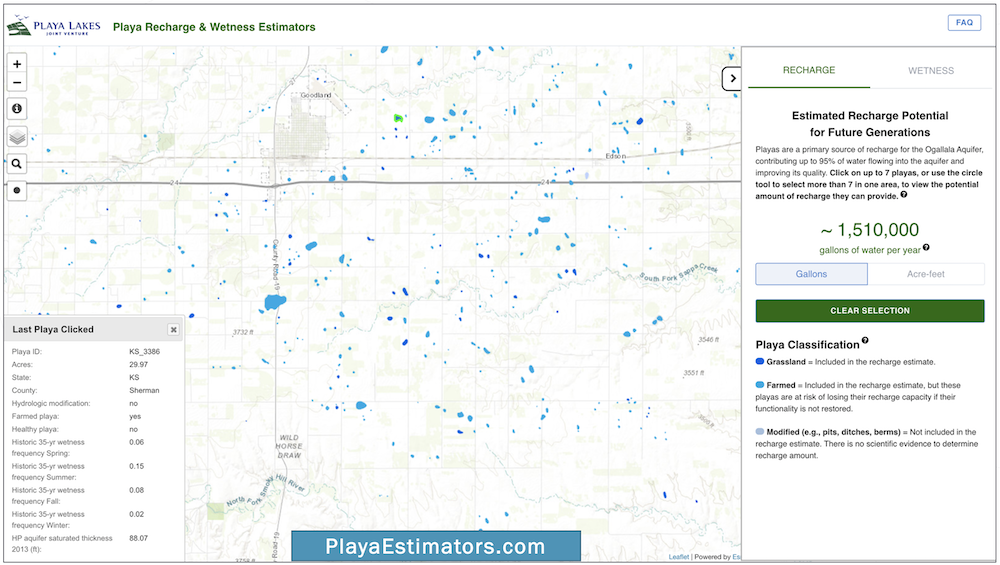 To learn how to use these tools, watch the Recharge Estimator tutorial and Wetness Estimator tutorial videos.
To learn how to use these tools, watch the Recharge Estimator tutorial and Wetness Estimator tutorial videos.
 Dale Schmidt
Dale Schmidt"The wetland is productive when you don’t get too much rain, but drought years are the best years."
In a normal year's precipitation, Dale says he might have been planting in mud or harvesting in mud, and with the cost of inputs these days, well. . .
“I decided to enroll it in a Wetlands Reserve Easement; I went with a lifetime perpetual easement. On a normal year, I was going to lose to flooding maybe 25% of that crop. So I decided to enroll. Since then, I’m very pleased. I put back into conservation what really should have probably stayed in something like that. It is a low lying, very heavily clayed property.”
This project is reaching well beyond the property boundaries to improve watershed health, to help recharge the Equus Beds Aquifer, and to provide wonderful habitat for migratory birds and other wildlife.
 Chester Peterson
Chester Peterson“This land is historic. Spanish explorer Francisco Vasquez de Coronado came north out of Mexico looking for seven silver cities this Indian told him about. He got up to central Kansas, and being human, you know he’s going to go to the highest point of land in the area to look further north and east for a village or city. On a full-moon night, you might be up there and say, ‘Hey, Coronado may have walked here.’”
“If I put four wind turbines on that 1,335 acres, I would double what I’d make from grass rental, so I can see why it’s attractive to some people. But, you know, when you do that, you’re selling something. You’re selling a part of yourself, a part of your heritage. With this perpetual easement, there can be no wind turbines or oil wells. There can’t be antennas. It can’t be sub-divided. It’s going to look just like it was in primeval times before the white man came. I wanted to preserve that.”
 Doug Duell
Doug Duell“One of my fields has a pretty large playa—we used to call them lagoons—and it seemed like every other year or so we’d get a big rain and that thing would fill up and whatever we planted would pretty much die by being submerged in water.”
The NRCS approached his dad about enrolling that wetland in a Wetlands Reserve Easement, which they did.
“Wildlife enhancement has a lot to do with it. If in fact it is replenishing the Ogallala Aquifer, that is super great! I realize it takes a lot of these [playas] to make a difference. It’s hard to imagine when you only have one, that when that [water] sinks down it’s going to help the aquifer, but every little bit helps.”
“It takes several good rains over the summer to keep it full, but we did notice there was a lot of wildlife came around there when it had water in it.”
We know that every decision by every landowner is a personal one, driven by unique experiences and circumstances. Understanding those decisions can only be appreciated through personal conversations. Our biologists are here to help—from identifying playa management options that fit with your operational goals to assisting with conservation program enrollment—at no cost to you.

We tour your playa, listen to your concerns and discuss your operational and habitat goals.

We explain various management and conservation options and discuss how they fit with your goals.

Based on your goals, we provide recommendations for programs or management changes.

We help you understand how each conservation program works and navigate the enrollment process.
These are a few of the conservation programs for playas. Visit our Conservation Programs page for more information or talk to a biologist to learn more about these and other options that may work for you.
Explore options for managing playas in fields that are typically farmed and determine how USDA conservation programs can meet your operational objectives. Download the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet (version 1.2, updated Feb. 14, 2022) and customize your calculations with individual operational costs, local rates for conservation programs, and more.
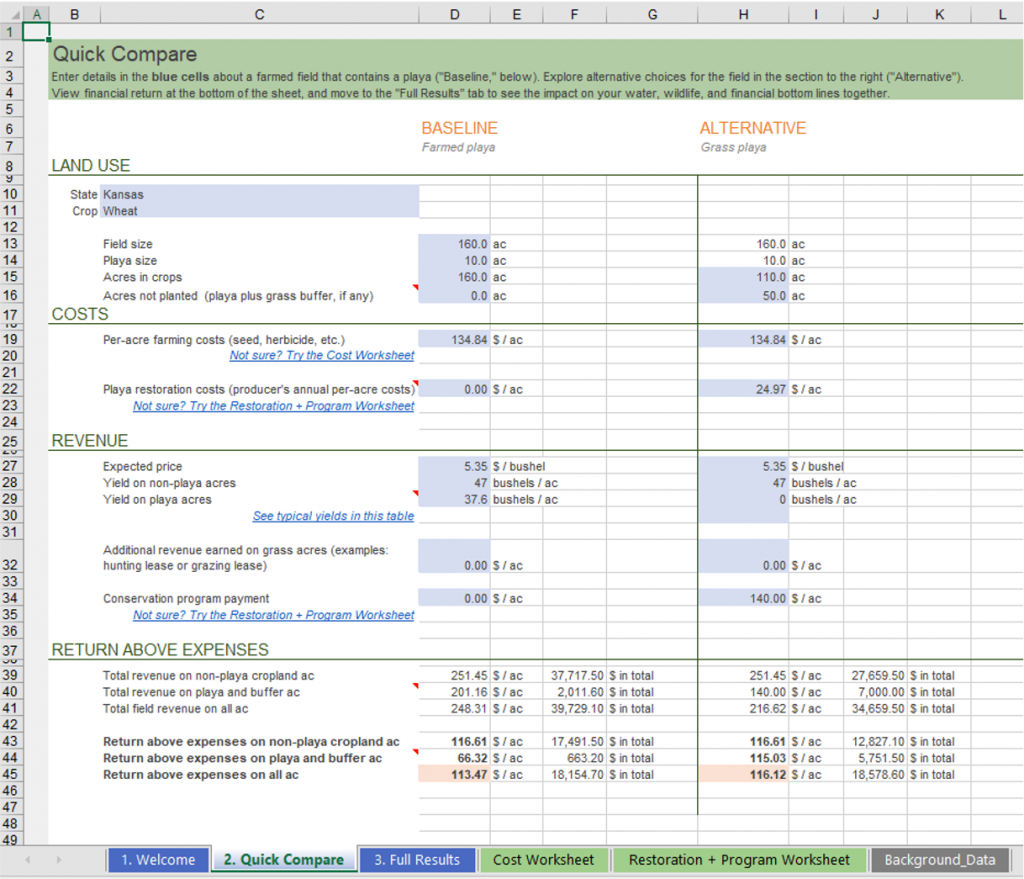 To learn how to use the calculator, watch the tutorial video.
To learn how to use the calculator, watch the tutorial video.
Looking for information about how to manage your playas? We can help you sort through the options, provide technical and financial assistance, and find the solution that is right for you. Contact one of our biologists listed below, send us a message or call the Private Landowner Habitat Assistance line at 844.422.2778.




















